While we know high body temperature, subsequent fever and a continuous dry cough are some of the most established symptoms of Covid-19, the World Health Organization (WHO) is now looking into how common it may be for infected people to experience a loss of smell (anosmia) or taste (ageusia). Thankfully, recent scientific studies show that from the Omicron variant on, these symptoms tend to disappear. Studies show that these types of disorders generally pass over time and patients should regain full functionality of the senses, although much depends on the extent of the initial impact of infection.
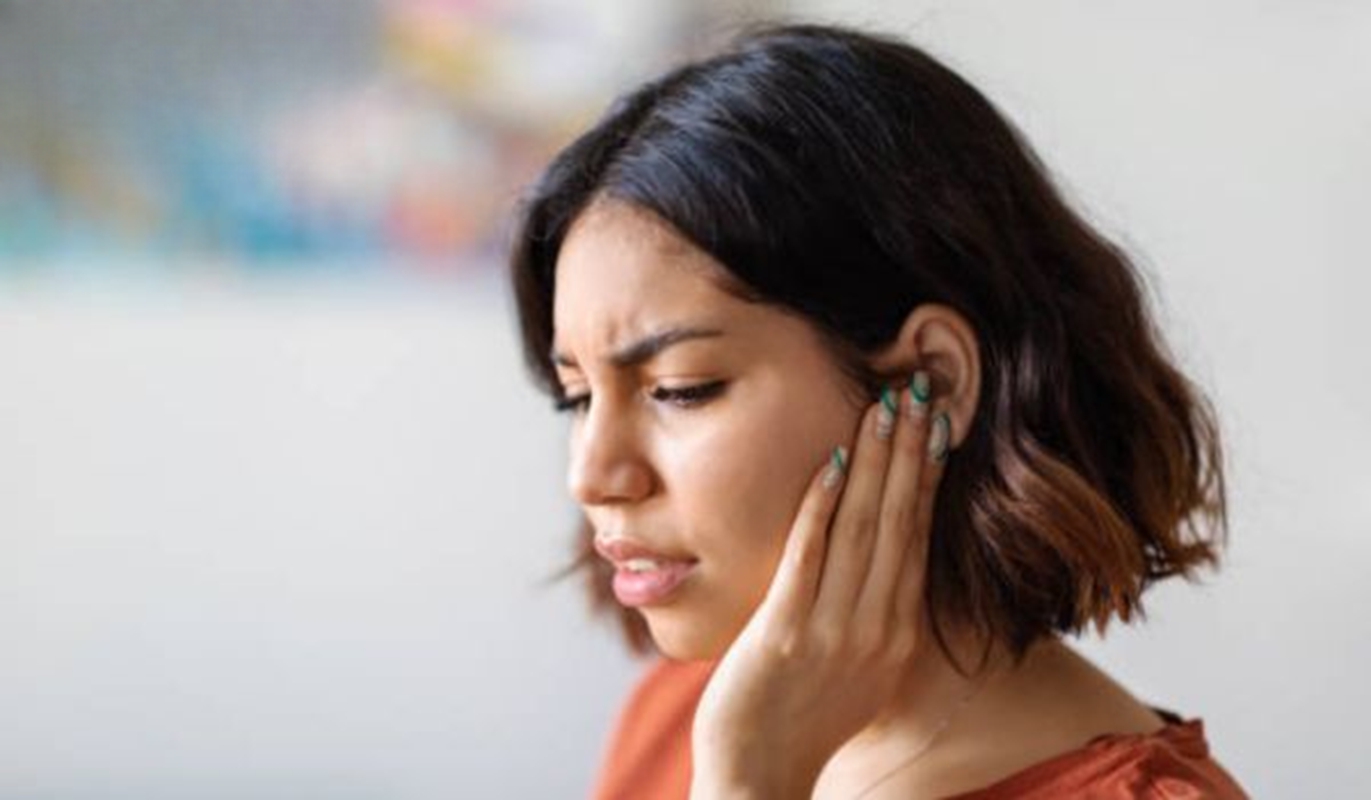
While hearing concerns are not generally reported among those infected with Covid, recent studies suggest that ear pain and excessive pressure in the ears may be one of the symptoms of Covid-19 and other ear-related conditions can be related to the virus onset.
Ear pain is one of the least common ear-related covid-19 symptoms. But, since the onset of the Omicron variant, its incidence has increased. This may be due to the fact that the new Covid-19 variants affect the upper respiratory tract more, thus facilitating the onset of symptoms related to the ear. The pain would be generated by the obstruction and the consequent inflammation that Covid-19 causes in the airways.
Indeed, when the upper part of the throat and nose are inflamed, these channels may become blocked thus causing the eustachian tube to no longer function correctly. In turn, this can give rise to discomfort in the ear and cause temporary hearing problems. Evidence for this was discovered by researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) and Massachusetts Eye and Ear, who reported evidence that Covid-19 can infect inner ear cells, including hair cells.
Probably the most common ear-related symptom of Covid-19 is excessive pressure in the ears and the feeling of clogged ears and ear popping. If you feel ear pressure or clogged ears, do not to use cotton swabs and Q-Tips because you risk making the situation worse.
This feeling of ear pressure, stuffy nose and clogged ear comes from the inflammation that the latest variants of Covid-19 cause in the upper airways. Since many of the symptoms of the virus are like flu ones, this excessive pressure inside the ear is most likely caused by clogged tubes in the ear due to the virus within the system.
More scientifically speaking, when the Eustachian tube (which connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx) becomes blocked, it can lead to a feeling of fullness and pressure in the ear, as well as ear inflammation and otitis media. Therefore, in most cases, once the effect of the virus has ended, the pressure inside the ears should normalize.
Here’s how Covid-19 may contribute to ear infections:
- Inflammation of the Eustachian tubes: Covid-19 can cause inflammation in the upper respiratory tract, including the Eustachian tubes that connect the middle ear to the throat. This inflammation can lead to fluid buildup in the middle ear, increasing the risk of ear infections;
- Secondary infections: People with Covid-19 may develop secondary bacterial infections, including ear infections, as a result of a weakened immune system or inflammation caused by the virus.
A sore throat and itchy ears can be associated with Covid-19, though they are not the most common symptoms. Here’s how they might be connected to the virus:
- Sore throat: Covid-19 often affects the upper respiratory tract, leading to inflammation of the throat. This can result in a sore throat, especially in the early stages of infection;
- Itchy ears: Although not a primary symptom of Covid-19, itchy ears may occur due to inflammation in the Eustachian tubes or sinus congestion. The virus can cause upper respiratory issues, leading to irritation in the ear canal or the connection between the ears and throat.
Ear and jaw pain on one side can occur in relation to Covid-19 due to several possible factors:
- Eustachian tube dysfunction: Covid-19 may cause inflammation in the upper respiratory tract, affecting the Eustachian tube, which helps equalize pressure in the middle ear. Inflammation or blockage of this tube can lead to ear pain;
- TMJ (Temporomandibular Joint) stress: The stress and tension caused by illness, including Covid-19, can exacerbate issues with the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), which connects the jaw to the skull. This can cause pain in the jaw that sometimes radiates to the ear on the same side.
A rash behind the ears, though not common with Covid-19, has been reported in some cases due to skin issues during viral infections. Here are some connections to Covid-19:
- Covid-19 skin manifestations: The virus may trigger various skin rashes, including hives or red patches, as part of the body's immune response;
- Sweat and irritation: Fever can lead to sweating, causing skin irritation or heat rash behind the ears, especially with prolonged mask use;
- Allergic reaction to medication: Some medications for Covid-19 may cause allergic reactions, resulting in rashes that can appear behind the ears.
Tinnitus is the condition of hearing sounds such as ringing or buzzing in the ears, but it can also manifest as the sensation of ears popping or crackling, especially in the case of Covid-19. Here are the main ways the virus may cause or worsen this condition:
- Inflammation and nerve damage: Covid-19 can cause inflammation in the body, including the auditory system. This inflammation might affect the auditory nerve or inner ear structures, leading to tinnitus;
- Stress and anxiety: Covid-19, and the stress or anxiety related to illness or the pandemic, can worsen or trigger tinnitus, as stress is a known factor in the development of ear ringing.
The association between Covid-19 infection and vertigo and dizziness was initially theorized and confirmed by a study by the University of Manchester and the Manchester Biomedical Research Center, published in the "International Journal of Audiology". The results of the study state that among patients with Covid-19, 7.2% indicate the presence of vertigo as a symptom.
Subsequently, on July 20, 2022, the article “The Prevalence of Dizziness and Vertigo in COVID-19 Patients: A Systematic Review” attempted to pool all the data from 14 previous studies related to vertigo and dizziness as a symptom of Covid-19. 4 of these studies generated case reports, and in all of them, vertigo and dizziness were detected as initial symptoms of Covid-19, preceding those relating to the respiratory tract, which occurred later.
These symptoms usually disappear at the end of the virus infection, however, they can rarely persist in the event of long Covid, as reported in the Manchester study and by Maslovara et al. The study “Post-COVID-19 Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo” revealed the possible persistence of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo after Covid-19.
Long Covid, or post-Covid syndrome, can lead to various ear-related issues in some individuals. These problems may include:
- Tinnitus: Persistent ringing, buzzing, or hissing in the ears has been reported as a symptom of long Covid;
- Hearing loss: Some people experience temporary or, in rare cases, lasting hearing loss due to the virus's impact on the auditory system;
- Ear pressure or clogged ears: Long Covid may cause ongoing inflammation or Eustachian tube dysfunction, leading to a sensation of ear pressure or blockage;
- Ear pain: Lingering congestion or inflammation from the virus can lead to discomfort or pain in one or both ears;
- Dizziness or vertigo: Damage to the inner ear or nerve inflammation can result in dizziness or balance issues, a condition known as vestibular dysfunction.
If these symptoms persist, consulting a healthcare provider or an audiologist is recommended to evaluate and manage ear-related issues caused by long Covid.
The above is the interpretation of COVID-19 and Your Ears: What the Research Says About Pain and Pressure provided by Chinese hearing aid supplier Shenrui Medical. Link https://www.srmcm.com/Blog/COVID-19_and_Your_Ears_What_the_Research_Says_About_Pain_and_Pressure.html of this article is welcome to share and forward. For more hearing aid related information, please visit Blog or take a look at our Hearing aids products