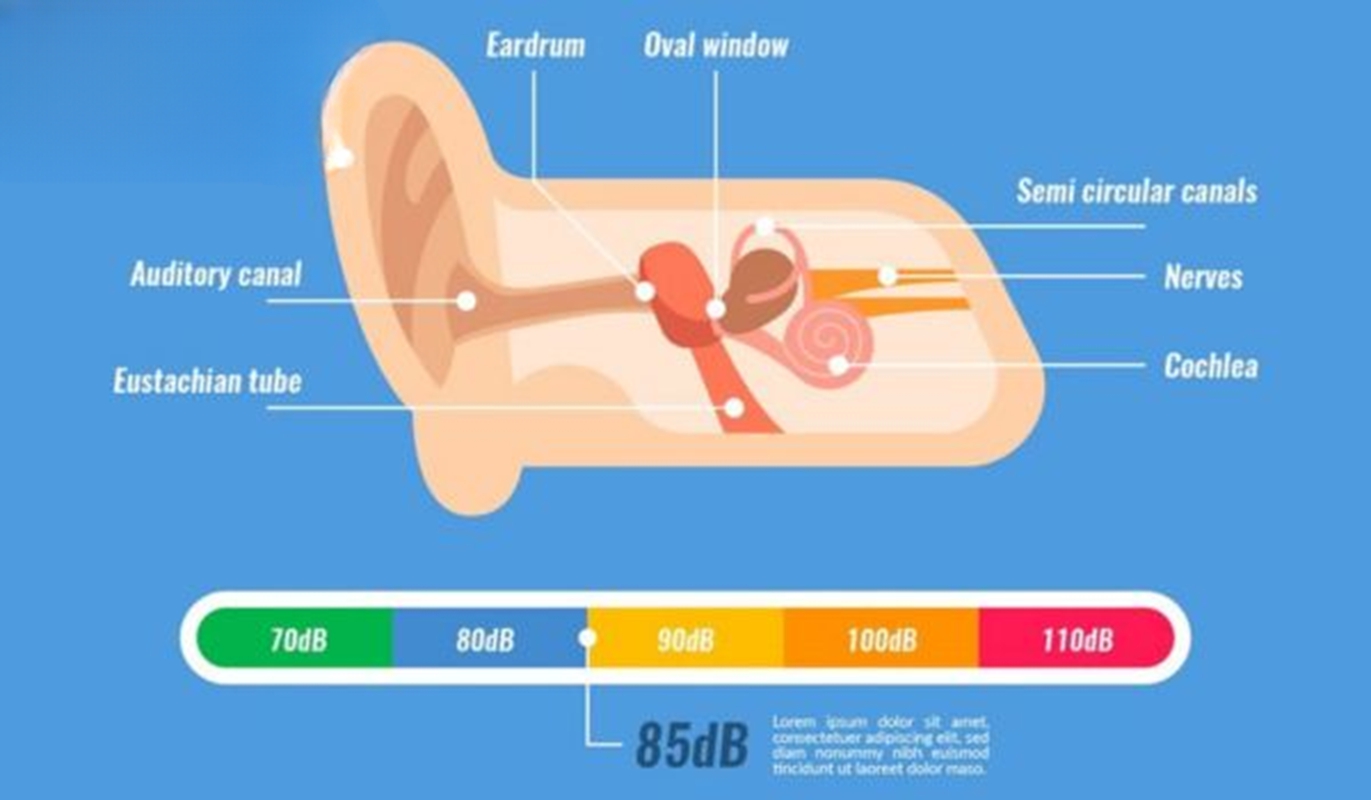
The eardrum, also known as the tympanic membrane, is a vital part of the auditory system, playing a crucial role in how we hear and maintaining ear health. This delicate membrane serves two primary purposes: transmitting sound waves from the outer ear to the middle ear and acting as a protective barrier against debris, water, and harmful pathogens. By converting sound vibrations into signals that can be processed by the inner ear, the eardrum ensures the clarity and precision of our hearing.
Understanding the function of the eardrum is essential for appreciating its role in the auditory process. It works in harmony with other ear components, amplifying and directing sound waves while safeguarding the middle ear from external damage. This blog explores the intricate workings of the eardrum, its importance in hearing, and the steps you can take to keep it healthy and functioning optimally.
What is the Eardrum?
The eardrum, or tympanic membrane, is a thin, flexible layer located between the outer and middle ear. It is responsible for separating the external auditory canal from the middle ear.
Structure of the Eardrum:
- Made of delicate tissue and arranged in a circular shape.
- Linked to three small bones in the middle ear: the malleus, incus, and stapes.
- Extremely sensitive to sound waves and vibrations, enabling it to play a crucial role in the hearing process.
What is the Function of the Eardrum?
The eardrum performs two primary functions:
Transmitting Sound Waves:
- The eardrum vibrates in response to sound waves entering the ear canal.
- The vibrations are passed to the ossicles in the middle ear, which amplify them and transmit them to the inner ear.
Protecting the Middle Ear:
- Acts as a barrier to prevent debris, water, and pathogens from entering the middle ear.
- Helps maintain the ear’s internal environment.
How Does the Eardrum Work?
The eardrum is an intricate mechanism that ensures seamless auditory processing. Here’s how it works step-by-step:
Step | Description |
Sound Reception | Sound waves pass through the ear canal and strike the eardrum. |
Vibration Generation | Sound waves pass through the ear canal and make the eardrum vibrate. |
Transmission | Vibrations travel through the ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) in the middle ear. |
Inner Ear Processing | The amplified sound reaches the cochlea for conversion into electrical signals. |
Signal Transmission | Electrical signals are sent to the brain via the auditory nerve for interpretation. |
This process highlights the precision of the eardrum and its role in ensuring clear hearing.
Role of the Eardrum in Hearing
- Amplifies Sound Waves: The eardrum enhances faint sound waves, converting them into vibrations that can be processed by the auditory system, ensuring clear and audible hearing.
- Enables Directional Hearing: By working with the brain and auditory nerve, the eardrum helps identify the direction and source of sounds, aiding spatial awareness.
- Protects the Middle Ear: Acting as a barrier, the eardrum shields the middle ear from debris, water, and pathogens, reducing the risk of infections and damage.
- Facilitates Sound Transmission: The eardrum transfers vibrations to the tiny bones in the middle ear (ossicles), which amplify the sound before passing it to the inner ear for processing.
- Maintains Balance and Hearing Clarity: A healthy eardrum ensures balanced hearing and stability, while damage to it can lead to reduced hearing clarity and potential balance issues.
If the eardrum is damaged, it can significantly affect hearing clarity and balance. If you experience any issues, it’s important to consult with an audiologist for immediate care.
Common Eardrum Issues and Their Causes
Ruptured Eardrum:
- Causes: Loud noises, ear infections, or inserting objects into the ear.
- Symptoms: Pain, hearing loss, and possible discharge.
Eardrum Infections (Otitis Media):
- Causes: Bacterial or viral infections.
- Treatment: Antibiotics or drainage procedures if necessary.
Eustachian Tube Dysfunction:
- Causes: Allergies, colds, or sinus infections causing pressure imbalances.
- Symptoms: Muffled hearing and a sensation of fullness in the ear.
- Pro Tip: Regular check-ups at a hearing care clinic in Delhi can help diagnose and treat these issues early.
Tips for Maintaining a Healthy Eardrum
- Avoid Inserting Objects into the Ear: Refrain from using cotton swabs, hairpins, or other sharp objects to clean the ear canal. This can damage the delicate eardrum and push debris further inside, increasing the risk of injury or infection.
- Protect Against Loud Noises: Use earplugs or noise-cancelling headphones when exposed to loud environments, such as concerts or noisy workplaces. This precaution helps prevent noise-induced damage to the eardrum and hearing.
- Keep Ears Dry: Protect your ears from water by wearing earplugs while swimming or showering. Keeping the ears dry reduces the risk of water-related infections, such as swimmer’s ear, that can impact the eardrum.
- Practice Safe Listening Habits: Lower the volume when using headphones or earbuds. Prolonged exposure to loud music can strain the eardrum and lead to hearing issues over time.
- Schedule Regular Check-ups: Visit an audiologist or ear specialist for routine ear health assessments. Regular monitoring ensures early detection of potential issues, helping you maintain healthy and functional eardrums.
When to Seek Help for Eardrum Issues
- Persistent Ear Pain: If you experience ongoing ear pain that does not improve, it could indicate an underlying issue such as an infection or injury. Persistent discomfort should never be ignored and requires professional evaluation.
- Muffled or Decreased Hearing: Difficulty hearing clearly or experiencing muffled sounds may suggest a problem with the eardrum, such as damage or obstruction. Early assessment can help restore hearing and prevent further complications.
- Symptoms of Infection: Redness, swelling, or unusual discharge from the ear are common signs of an infection. These symptoms require prompt medical attention to prevent the infection from spreading or causing long-term damage.
- Feeling of Fullness in the Ear: A sensation of fullness or pressure in the ear may be caused by fluid buildup or eustachian tube dysfunction. Consulting a specialist can identify the root cause and provide effective treatment.
- Hearing Loss with Dizziness or Tinnitus: Hearing loss accompanied by ringing in the ears (tinnitus) or dizziness could point to a more serious condition involving the eardrum or inner ear. Seeking immediate care ensures proper diagnosis and management.
Conclusion
The eardrum plays a vital role in the auditory system by transmitting sound waves, amplifying them, and protecting the middle ear. Its health is crucial for maintaining clear hearing and overall ear function.
If you’re experiencing any ear-related issues, don’t wait. Visit our hearing care clinic and consult with an audiologist for expert guidance and care. Protect your ears—they’re your gateway to the sounds of the world!