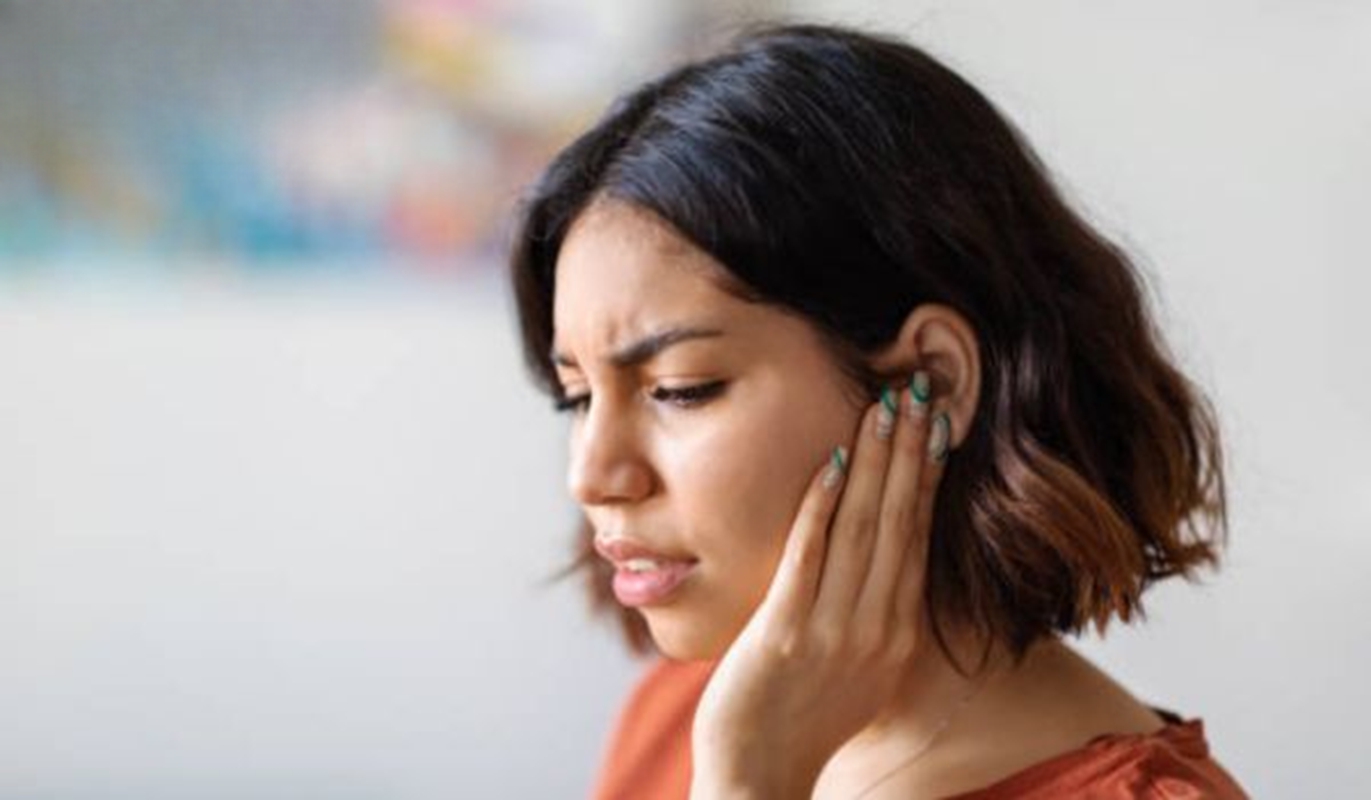
You can get colds or the flu at any time of the year, but the viruses that cause these common respiratory illnesses tend to spike in the fall and winter months. Most people who suffer from cold and flu can expect coughing, congestion, sore throat or mild fever. But what does it mean if you experience a cold and ear pain simultaneously, or even a combination of flu and ear infection?
Ear discomfort might not be as common as other cold and flu symptoms, but it can be just as serious and even a precursor to more severe complications. Keep reading to learn how to recognize, treat and prevent ear-related symptoms related to a cold or the flu.
Cold symptoms with blocked ears typically occur due to congestion affecting the Eustachian tubes. Common symptoms include:
Nasal congestion: A blocked or runny nose is a primary cold symptom, contributing to ear blockage;
Sore throat: Irritation in the throat may accompany ear discomfort due to connected passages;
Coughing: Mucus from the cold can trigger coughing, potentially adding pressure to the ears;
Ear fullness: A sensation of pressure or fullness in the ears due to blocked Eustachian tubes;
Muffled hearing: Temporary hearing loss may occur because of fluid buildup or pressure changes;
Headache: Sinus pressure from congestion may lead to headaches, which can also affect the ears;
Sneezing: Frequent sneezing, a common cold symptom, can worsen ear pressure temporarily.
Can a cold cause tinnitus? Tinnitus is characterized by ringing, hissing or buzzing in the ears. You might notice new or increased tinnitus after a particularly nasty cold. This might be caused by increased pressure in your ears that can accompany a cold or sinus infection. If you continue to experience tinnitus after a cold, contact your doctor.
Ear congestion during a cold can cause muffled or reduced hearing. If congestion leads to an ear infection, you might experience temporary hearing loss. Typically, hearing loss from cold will resolve as the virus clears your system. Treat hearing loss from cold with:
Decongestants like pseudoephedrine (Sudafed);
Saltwater gargle;
Warm compress.
Labyrinthitis is inflammation of the inner ear and the nerves that connect it to the brain. A viral infection, including a cold, can trigger it. The condition can cause dizziness, nausea and hearing loss, which resolves after a few weeks. Rest, avoid sudden movements and ask your doctor about medications to manage nausea. If symptoms of labyrinthitis after a cold persist, consult with your healthcare provider.
Another common response to the inflammation that accompanies a cold is itchy ears. Use over-the-counter ear drops to relieve symptoms of itchy ears with a cold. Never insert anything in your ear.
When your ear is infected, fluid and pus can build up and cause the eardrum to rupture. This might lead to bleeding or drainage from the ear. Keep the ear dry and avoid putting any objects in your ear. If bleeding or drainage from the ear after a cold happens or is accompanied by changes in hearing, contact a medical provider immediately.
Congestion from a cold can block the Eustachian tubes, causing fluid to build up in the ear. Fluid in ear symptoms include a feeling of fullness, ringing or popping sounds, difficulty hearing or balance issues.
Clogged ears from a cold often result from congestion in the Eustachian tubes, which connect the middle ear to the back of the throat. This congestion can create a feeling of fullness, muffled hearing, or pressure in the ears. It’s common to experience temporary hearing difficulties and discomfort, especially when swallowing or yawning. These symptoms usually subside once the underlying cold or infection clears.
Earache during a cold is usually caused by the swelling and congestion of the Eustachian tubes, which leads to pressure buildup in the middle ear. This pressure can result in a dull or sharp pain, sometimes accompanied by a feeling of fullness or blockage. In some cases, the pain may be persistent or worsen with certain movements, like swallowing or yawning.
The common cold and ear infections are closely related. A cold, caused by a viral infection, often leads to nasal congestion and swelling in the Eustachian tubes, which connect the throat to the middle ear.
This congestion can trap fluid in the middle ear, creating an environment conducive to bacterial growth and resulting in an ear infection. Symptoms of an ear infection may include ear pain, pressure, and muffled hearing, which can develop alongside or following cold symptoms.
Ears popping during a cold is common due to pressure changes in the Eustachian tubes. Nasal congestion can block these tubes, leading to a sensation of fullness and pressure.
When you yawn or swallow, the tubes may open, causing a popping sound as the pressure equalizes.If popping is accompanied by pain or hearing loss, consult a healthcare professional.
When treating fluid in the ear from cold or more severe complications like cold and ear pain or flu and ear infection, especially in children, consider the following:
Children under 4 shouldn’t be given cold medicine;
Consult a doctor before offering OTC medication to children under 6 months;
Use homeopathic remedies with caution. Essential oils like garlic, tea tree or olive oil pop up as solutions online but have not been shown to improve ear infections;
Never insert objects into the ear, including cotton swabs.
Most cold and ear pain will resolve once the virus has cleared your system. If symptoms persist, be sure to consult with your doctor for the best course of treatment.
The above is the interpretation of How to Unclog Ears Stuffed Up from a Cold or Sinus Infection provided by Chinese hearing aid supplier Shenrui Medical. Link https://www.srmcm.com/Blog/How_to_Unclog_Ears_Stuffed_Up_from_a_Cold.html of this article is welcome to share and forward. For more hearing aid related information, please visit Blog or take a look at our Hearing aids products