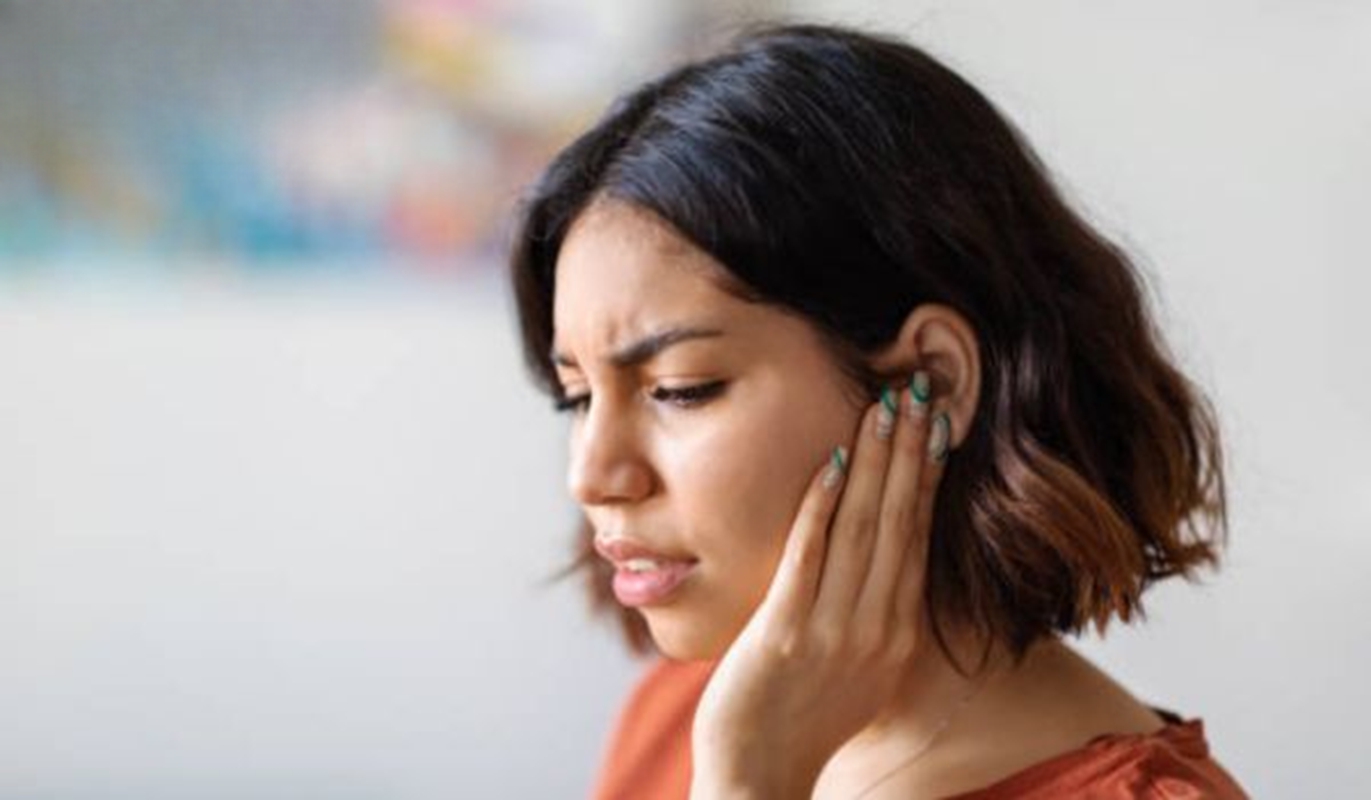
Unfortunately, having itchy ears is a common problem. All parts of the outer ear can be affected, including deep in the ear canal. In severe cases, the irritated skin can lead to plaques that affect hearing and cause further problems.
Here are the top reasons your ears might itch, and what do about it:

1. Seborrheic dermatitis of the ear (dandruff)
A common reason for itchy ears is a condition called seborrheic dermatitis, a type of rash that affects the sebaceous glands, which produce oil. It can occur on the scalp and eyebrows, and in the ears. A mild case of seborrheic dermatitis causes the skin to flake, known as dandruff. Yep, you can have ear dandruff!
When dermatitis is severe, the skin also may be red and intensely itchy. Your risk of seborrheic dermatitis increases with age, according to Dr. Steve Daveluy, associate professor and program director at Wayne State University School of Dermatology.
2. Infections
Numerous germs can infect the outer and middle ear. Itchy ears that are also painful, warm and red is a strong indicator of an infection, especially if you have other common symptoms like a fever.
One common type of itchy and painful infection is otitis externa, better known as "swimmer's ear." (You don't have to go swimming to catch an outer ear infection, though. Living in a humid environment puts you at risk, for example.)
3. Irritation from hearing aids, earbuds and AirPods

Scratching can make the problem worse.
So can over-cleaning the ears, which are
naturally self-cleaning.
Hearing aids, earbuds and AirPods can create itching and make conditions like dermatitis worse. With hearing aids, for example, the domes or earmolds can rub against the skin. They also block the ear canal, which can cause moisture buildup. Rarely, some people become allergic to a component of the hearing aid or earbud.
If your hearing devices cause your ears to itch, talk to a hearing health professional. They’ll examine the fit to make sure your devices are seated correctly. If the skin in your ears is dry, they may recommend using a product such as MiraCell ProEar, which makes hearing devices easier to insert and more comfortable to wear.
Also be sure to clean your hearing aids and hearing devices regularly. Ask your hearing care provider for guidance if you're not sure about how to clean hearing aids.
4. Earwax blockage
Earwax is normal and healthy, but in some cases it can become impacted and irritating, leading to an itchy sensation. One big reason for earwax blockages and other ear problems is over-cleaning. The ears are self-cleaning and self-protecting. The wax is a very important part of this protection. Anytime you put something in your ear, you may remove some of the earwax but also shove the earwax back down into the ear.
Over time, this can lead to an impaction and chronically itchy ears. (See below on how to get help.)
5. Contact dermatitis
Contact with common irritants such as hydrogen peroxide, rubbing alcohol, water, ear drops (both prescribed and over-the-counter), or excessive ear cleaning can all cause dry, itchy ears.
Some skin and hair products can irritate the skin, such as paraphenylenediamine, a chemical found in hair dye, according to the National Institutes of Health (NIH). So can certain metals in jewelry, especially nickel. One of the best ways to avoid ear dermatitis is to simply avoid the irritant.
Note: The NIH urges people not to use steroid creams on or around the face, which can cause the affected skin to weaken and loosen.
6. Food and seasonal allergies
Yep, food, skin and seasonal spring and fall allergies can all affect the ears, leading to the familiar itchy feeling many of us know know and hate. The ears are definitely not immune to allergies, unfortunately.
7. Skin disorders (including ear eczema and psoriasis)
These skin disorders can affect the skin within the ear canal, even deep inside near the eardrum. Eczema is the name for a group of conditions that cause patches of the skin to become red, itchy and inflamed.
According to the National Eczema Society, ear eczema can be irritating and painful. It can also occur in several different places. Near the earlobe is perhaps most common, but it also can affect:
- earlobes
- conchal bowl (the area outside the ear hole)
- ear opening (meatus)
- ear canal
- ear drum
Older adults can develop what's called asteatotic eczema, or dry, itchy and scaly skin, often caused by dry air or over-washing the skin.
Meanwhile, psoriasis, a chronic, autoimmune disease is characterized by a red, itchy rash on the skin, including the ears. The National Psoriasis Foundation urges people with psoriasis to be careful about treating psoriasis anywhere on the face or scalp, as the skin is very sensitive.
According to the physicians at My Psoriasis Team, there is a risk of temporary hearing loss if ear psoriasis is extensive or severe, so it's important to get proper treatment.
In some cases, seborrheic keratitis—non-cancerous dark growths on the skin—can grow in the ear, too.
Rare causes of itchy ears
Diabetes
Certain systemic disorders, such as diabetes, make a person more prone to ear infections and itchiness. This is because diabetes makes earwax less acidic, which makes the skin in the ears more vulnerable to fungal and bacterial infections.
It is extremely important to see a professional for treatment, as rinsing the ears with water or other fluids can make the situation worse.
Liver disease
Some liver diseases that block bile, such as primary biliary cholangitis and cholestasis, can make the skin very itchy, including the ears. However, generally the itching occurs all over the body, and not just the ears. A person is also likely to have other signs, like yellowing skin, fatigue and easy bruising, note doctors with The Center for Liver and Hepatobiliary Diseases at Mercy Medical Center.
How to treat itchy ears
If you have drainage, a bad smell, ear pain or noticeable inflammation, do not wait to seek professional help. These are indications of an infection or another serious problem, and correct diagnosis and treatment is important.
Scratching will make it worse
Meanwhile, whether the problem is serious or mild, don't put anything in your ears. While it’s tempting to insert something into your ear canal to scratch the itch, that’s exactly what you shouldn’t do. Not only do you risk damaging the eardrum and scratching the delicate skin of the inner ear, you also increase your urge to itch.
“Try not to scratch at all,” Dr. Daveluy said. “For any skin, scratching makes the nerves that feel itch grow. So the more you scratch, the more you’ll itch.”
The more you scratch, the more you’ll itch.
The same is true of putting water or other random liquids in your ear. That can make the problem worse.
Instead, try treating the underlying problem. If you have dandruff, try switching to a dandruff shampoo. If your itching flares up along with seasonal allergies, try taking an antihistamine. To alleviate dryness associated with over-cleaning the ears or earwax blockage, use a product like MiraCell.
If your condition is mild but doesn't clear up, see a doctor. Using a tool called an otoscope, a doctor or a hearing care provider can get a good look at the skin in your ear to see what's going on. They also can remove earwax, if needed.
Your family doctor can discuss your symptoms, examine your skin and determine the proper diagnosis to formulate an effective treatment plan. If you have a complicated case, you may be referred to a dermatologist or an ear, nose and throat physician.
Can you prevent itchy ears?
Overcleaning the ears often causes more problems than it solves
A common way people accidentally infect their ears is by scratching too hard or cleaning too hard, breaking the skin open with an unclean object, especially fingernails, cotton swabs, bobby pins, twisted cloths or ear candles. Be gentle with your skin! The ears are actually little self-cleaning ovens and don't need much help.
Wash your hands before handling hearing aids or similar devices, and avoid getting shampoos and soaps in the ear.
How to correctly clean your ears
It's simple: For the most part, you don't need to do anything except normal hygiene. Taking regular showers and letting letting the warm water and shampoo run over your ears every is probably enough to soften and loosen excess earwax. Dry your ears after your shower. A Q-tip or cotton swab is not necessary. If you do suffer from impacted ear wax, see a hearing care professional for in-clinic ear cleaning.
Why is the skin in our ears so sensitive?
The environment in your inner ear is unique and faces some “special challenges,”
“Because of the warmth and moisture, the ear canal is at a higher risk of infection by bacteria,” Dr. Daveluy said. “To protect against this, the skin of the ear canal has specialized oil glands (called ceruminous glands) that secrete earwax. Much like the nose, the ear canal also grows small hairs to help prevent debris from entering the ear.”
Ears can't sweat
Another unique attribute of inner ear skin is that it doesn’t contain eccrine sweat glands, the kind the rest of our body uses to secrete sweat when we’re warm or stressed. This, along with the waxy nature of cerumen, helps prevent moisture buildup in the canal.
Don’t let itchy ears prevent you from wearing your hearing aids
Itchy ears can be annoying, but they shouldn’t prevent you from wearing your hearing aids as prescribed. So often this condition is easily resolved, leaving you free to be part of every conversation—no matter what people happen to be saying. Sometimes all you need is special over-the-counter ear drops to protect your skin, or your hearing aid domes resized or refit.
If your hearing aids are causing problems or if you aren't hearing your best, schedule an appointment with a hearing care professional. For a complete list of hearing centers in your community, visit our online directory of consumer-reviewed clinics.
The above is the interpretation of Itchy Ears: 7 Common Causes and How to Find Relief provided by Chinese hearing aid supplier Shenrui Medical. Link https://www.srmcm.com/Blog/Itchy_Ears_7_Common_Causes_and_How_to_Find_Relief.html of this article is welcome to share and forward. For more hearing aid related information, please visit Blog or take a look at our Hearing aids products