What are hair cells?
Hair cells are small sensors in our ears that receive sound signals and send them off to the brain. Each ear has roughly 15,000 hair cells in total. Around 3,000 of these hair cells are inner hair cells, and the other 12,000 are outer hair cells. Inner hair cells receive the sound signals and translate them, and outer hair cells work to amplify the sounds that come into the ear.
Where can hair cells be found, and how do they work?
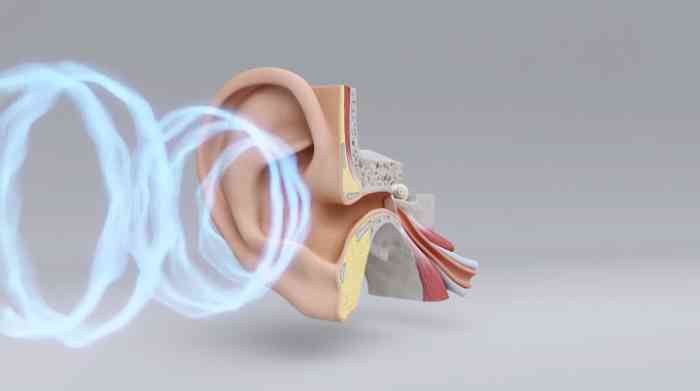
The cochlea is filled with fluids and lined with hair cells. Sound vibrations that come from the middle ear are transferred to the fluids in the cochlea, and the hair cells pick up these vibrations and convert them into electrical impulses. These electrical impulses are then transferred to your brain. Hair cells can also be found in the semicircular canals, which are a part of the inner ear that help with balance. These hair cells detect the motion of the fluids that are in the semicircular canals to help you maintain your sense of balance.
What happens when hair cells are damaged?
All of the hair cells in our ears are fully developed in the fetal stage and do not regenerate, which means that we can only lose hair cells once we are born. We naturally lose our hair cells as we age, but they can also be damaged through exposure to loud noises, chronic infections, and certain medications. Damage to hair cells can lead to irreversible hearing loss. While age-related hearing loss is inevitable, there are steps you can take to prevent the risk of losing hair cells by other means. Using ear protection devices such as earmuffs or earplugs in loud settings can be helpful when caring for your ears and preventing noise-related hair cell damage. Regular check-ups with an audiologist are also good for catching the signs of hearing loss at an early stage.
The above is the interpretation of The Amazing Journey of Sound: From Ear to Brain provided by Chinese hearing aid supplier Shenrui Medical. Link https://www.srmcm.com/Blog/The_Amazing_Journey_of_Sound_From_Ear_to_Brain.html of this article is welcome to share and forward. For more hearing aid related information, please visit Blog or take a look at our Hearing aids products