Earwax serves an essential function in protecting and cleaning our ears. However, excessive earwax can sometimes cause blockages, leading to pain, ringing in the ears (tinnitus) and even hearing loss. Knowing how to recognize and resolve earwax blockages can help you find relief quickly.
Earwax, or cerumen, is a waxy substance produced by the glands in your ear canal. The body naturally makes earwax to coat, protect and lubricate the lining of the ear canal. Earwax can also trap dust and bacteria, preventing small objects from entering and damaging the ear. Without earwax, our sensitive ear canals would be vulnerable to harmful germs, dust and objects that could cause infections or damage.
Even though earwax is naturally occurring and crucial to the health of our ears, there’s a delicate balance between the right amount and too much. When too much earwax buildup is in the ear canal, you may experience earwax blockage, also known as cerumen impaction.
Earwax is naturally designed to make its way to the opening of your ear and be washed away or fall out on its own. When this doesn’t happen as it should, you get earwax buildup.
But what causes earwax buildup? Some people naturally produce more earwax than the body can efficiently get rid of, which can lead to buildup. In many cases, earwax buildup is due to external factors, such as wearing earplugs, earbuds or hearing aids that are placed inside the ear canal and can disrupt the movement of earwax.
Earwax blockage can also happen if you use Q-tips to get earwax out on your own. Instead of removing wax, you’re more likely to push it deeper into the ear canal, causing it to become impacted.
How do you know if you have earwax buildup? While earwax is normally helpful, it can sometimes build up and cause blockages, leading to discomfort and other noticeable symptoms.
One of the most common signs of earwax buildup is a sensation of fullness or pressure in the ear. You might also notice a reduction in hearing, with sounds seeming muffled or distant. Other possible symptoms include ringing in the ears (tinnitus), itching, dizziness, or even mild ear pain. These symptoms can affect one or both ears and may develop gradually over time.
People who use hearing aids or earphones may find that wax buildup interferes with sound quality or causes whistling noises due to feedback. If your hearing aid suddenly seems less effective, earwax may be the cause .
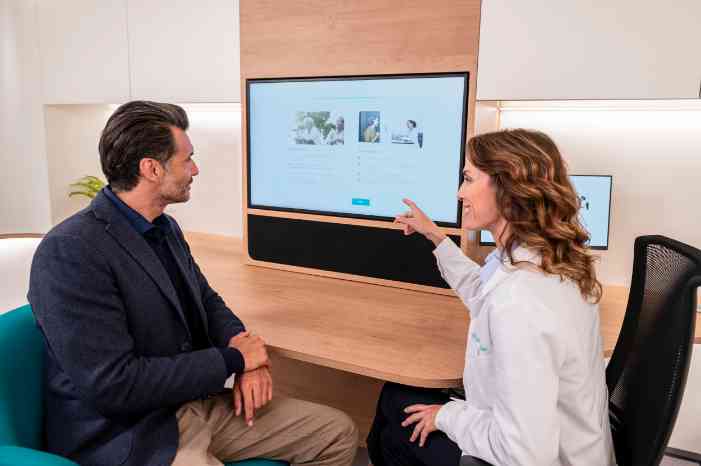
It’s important to avoid inserting cotton swabs or other objects into your ears to remove wax. This can push the wax further in and worsen the blockage. If symptoms persist or become bothersome, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional. They can safely examine your ears and remove any excess wax using specialized tools or techniques like microsuction.
Keeping up with regular ear care—especially if you wear hearing aids—can help prevent buildup and keep your ears healthy.
Earwax blockage is one of the most common causes of conductive hearing loss—the term for hearing loss caused by issues that prevent sound from being delivered to and through the ear canal, ear drum or middle ear. Other earwax blockage side effects include:
- Ear pain or ache
- The feeling of fullness in the ear
- Ringing in the ear (tinnitus)
- Discharge or odor
- Dizziness
- Itchiness
- Ear infection
You may be more likely to develop impacted earwax if;
- You have narrow ear canals
- You have a lot of ear hair, dry or hard earwax
- Your body naturally produces an excess of earwax
What else causes impacted earwax? Having foreign objects in the ear, such as hearing aids or headphones, can stimulate wax production and keep wax from naturally falling out on its own, potentially leading to impacted earwax.
Hearing aid wearers are often at higher risk of developing impacted earwax because the devices prevent wax from falling out naturally. If you wear hearing aids and experience issues such as feedback, poor fit or reduced effectiveness, earwax may be the culprit.
Excessive earwax not only affects your ears but can damage your devices. In fact, excessive earwax is one of the most common causes of hearing aid malfunction. If you notice a buildup of earwax in your hearing aids, you might need to clean your devices more often. Follow these steps to clean your hearing aids and keep them wax-free:
- Use a special brush from your hearing care professional to clear away wax on the earpiece and a pick or multi-tool to remove the particles inside.
- Wipe down the outside of your devices with a soft, dry cloth.
- Store your devices in a drying chamber overnight.
- Regularly check and change your hearing aid wax filters.
If you want more information on what dissolves earwax from hearing aids or how to properly care for your hearing aids at home, talk to your hearing care professional at your local Miracle-Ear store.
The amount of earwax your body produces is unique to you. There is no specific amount that is considered “too much,” but some people do produce more earwax than the body needs to coat and protect the ear canal.
If the amount of earwax you produce causes frequent impaction or you start to notice symptoms of impacted earwax, see your healthcare provider to discuss removal techniques.
Learning how to prevent wax buildup in ears can save you from experiencing painful impaction.
To start, avoid cleaning your ears with foreign objects like cotton swabs. If you can, limit the use of earbuds or earplugs, as any foreign object can trigger increased earwax production. If you rely on hearing aids, be sure to keep your ears as clean and dry as possible and follow the advice of your hearing care provider on how to clean and care for your device.
It’s also important to have regular checkups with your doctor or hearing care provider to make sure earwax is not building up and causing hearing loss to worsen.
While there’s no such thing as an earwax doctor, the following professionals can help you with earwax problems or direct you to a specialist who can:
- Licensed practical nurse (LPN)
- Registered nurse (RN)
- Otolaryngologist (ENT)
- Audiologist
- Miracle-Ear hearing care professional (HCP)
See a medical professional right away if you experience any of the following symptoms:
- Ear pain
- Sudden hearing loss
- Dizziness
- Cough
- Itchiness
- Odor or drainage from the ear
- Bleeding from the ear
Taking care of your ear health is important, but doing it in the right way is crucial. Don’t let problems go untreated, and keep up a regular schedule of annual hearing tests to stay on top of your hearing health for the long term.
The above is the interpretation of The Complete Guide to Dealing with Impacted Earwax provided by Chinese hearing aid supplier Shenrui Medical. Link https://www.srmcm.com/Blog/The_Complete_Guide_to_Dealing_with_Impacted_Earwax.html of this article is welcome to share and forward. For more hearing aid related information, please visit Blog or take a look at our Hearing aids products