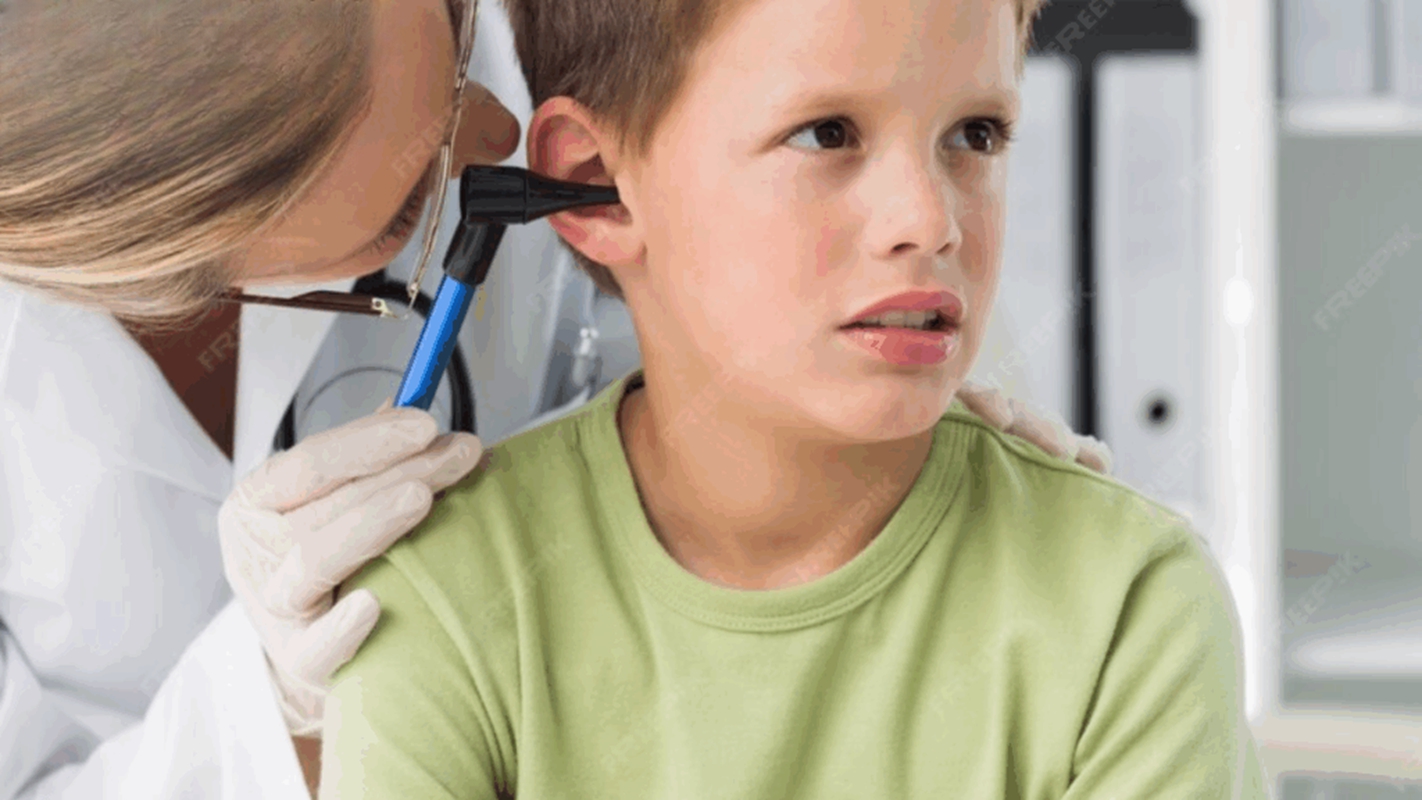
Hearing loss in children impairs speech development and learning abilities while producing behavioural patterns and difficulties with social communication. The disability of mild hearing loss slows down language development and reduces performance in academic work and life communication. Early detection remains essential to achieve positive treatment results.
Hearing-impaired individuals benefit from appropriate support to follow typical life trajectories. The analysis investigates what causes child hearing loss, together with its warning signs, available treatment choices and contains adapted guidance for parental early detection and fast resolution of the condition.
What Is Hearing Loss in Children?
The inability to detect sounds by children in either one or both ears represents hearing loss. The condition appears either at birth as a birth defect or develops afterwards because of medical conditions or injuries. The extent of hearing impairment, with its degree of severity, determines how children develop speech and language skills and learn new information.
Common Signs of Hearing Loss in Children
In babies:
- Unstartled by loud noises
- Not turning to follow the sound
- Delayed babbling or cooing
In toddlers or older children:
- Delayed speech
- If one observes a child struggling to attend to simple commands or instructions
- Frequent turning up of the volume on their electronic devices
- Distracted and behavioural issues
If you would like more information on conducting a preliminary assessment with your child, you could read about How to Test a Baby’s Hearing at Home.
Types of Hearing Loss in Children
- Conductive Hearing Loss: Sound transmission failure across the outer and middle ear creates this specific type of hearing loss. Multiple factors result in hearing loss, such as ear infections combined with fluid building up behind the eardrum or a buildup of earwax. Treatment can resolve hearing issues that lead to temporary conductive hearing loss.
- Sensorineural Hearing Loss: People develop sensorineural hearing loss from inner ear or auditory nerve damage, which most often results in permanent hearing impairment. Sensorineural hearing loss develops because of three main reasons: genetic factors, heavy noise exposure, or a viral infection.
- Mixed Hearing Loss: People with mixed hearing loss experience both conductive and sensorineural problems in their ears. People with mixed hearing loss endure similar auditory difficulties at all levels between their outer and middle ear and their inner ear or auditory nerve.
Hearing loss in children can be caused by several factors, including:
- Genetic causes: passed down conditions that impact the ear structure and how it works
- Infections such as meningitis, measles, and chronic ear infection.
- Loud noises: Prolonged or repeated exposure to loud sounds damages hearing.
- Complications during birth: Late preterm, prematurity, and low birth weight.
- Some medications: These drugs are called ototoxic, primarily being harmful to hearing.
Impact on Child Development
Hearing loss can profoundly affect a child’s development:
- Speech and Language Delay: Having trouble developing clear speech or understanding language.
- Academic Difficulties: Can hardly read, write, and/or learn.
- From talking to social isolation: Almost no interaction with others.
Diagnosing Hearing Loss in Children
Early diagnosis is vital. Hearing tests vary based on age:
Age Group | Recommended Test | Purpose |
0–6 months | Otoacoustic Emissions (OAE), Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR) | Assess inner ear and auditory nerve function. |
6 months–2 years | Visual Reinforcement Audiometry (VRA) | Observe behavioural responses to sounds. |
2–5 years | Conditioned Play Audiometry (CPA) | Engage the child in play-based hearing tests. |
5+ years | Pure Tone Audiometry | Determine the faintest tones a child can hear. |
Knowing the Degree of Hearing Loss helps understand how serious it is and what treatment options are best.
Treatment Options
- Medical Treatment: Antibiotics in case of infections or surgery if structural abnormalities exist.
- Hearing Aids: Devices to amplify sound, depending on the degree of hearing impairment.
- Cochlear Implants: Electronic devices for severe sensorineural hearing loss.
- Speech Therapy: Assisting children with communication skills.
- Educational Support: Extending special educational services to include adaptations in the classroom.
Prevention and Care Tips
- Regular Check-Ups: Regular hearing screenings, especially if family history is present.
- Protection Measures: Use ear protection when in noisy environments.
- Avoid Ototoxic Medications: Check with your doctor before administering any medicine known to affect hearing in your child.
- Treatment Promptness: Immediate management of ear infections and related ear problems.
Conclusion
Children who are detected for hearing loss earlier in life are able to manage their hearing loss. Early access to medical care and informed understanding of symptoms, causes, and types of hearing loss are all factors that can help improve children’s quality of life. Children with hearing losses need to have periodic screenings and receive preemptive care, allowing them to obtain appropriate support.
For more information on related topics, consider reading about high-frequency hearing loss.