Key points:
-
Diplacusis, also known as double hearing, is a rare condition that causes a single sound to be perceived as two different pitches.
-
It's more likely to affect people with hearing loss or ear problems, especially those who have asymmetrical hearing loss.
-
While it can be concerning, treating the cause of double hearing usually stops or minimizes symptoms.
For most people, our ears work together, delivering sounds as one "unit" to our brain. Even if the ears perceive slightly different pitches, our brain still can interpret it as the same source of sound. This is similar to how our eyes work—we see one visual field, instead of two.
However, just as people can experience double vision, people can also experience double hearing.
What is double hearing?
The medical term for double hearing is diplacusis binauralis. People with this condition perceive one sound as two distinct pitches. It may or may not be accompanied by tinnitus, or ringing in the ears.
As you can imagine, this sensation can be disturbing and troubling to those who experience it. It can affect anyone, but having certain conditions make it more likely to occur.
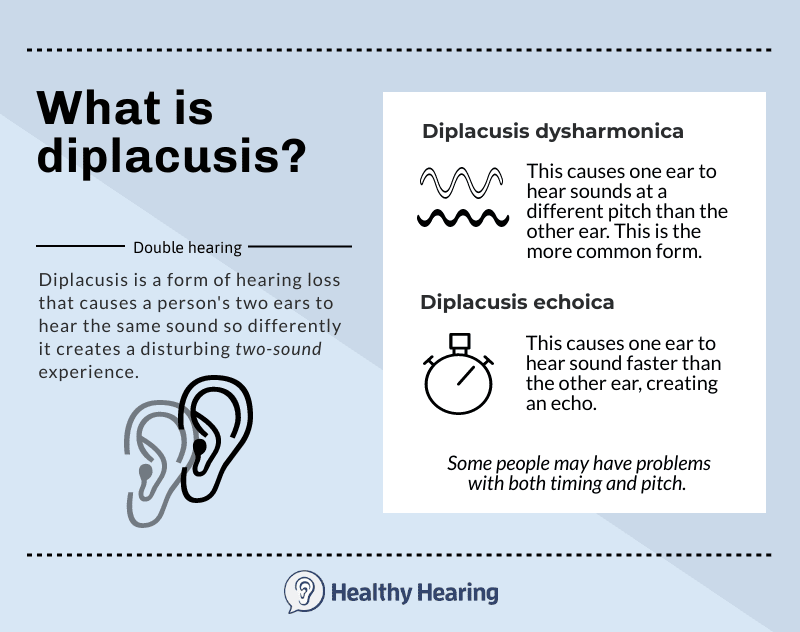
Double hearing can occur in both ears or it can affect just one ear, which is known as diplacusis monauralis. More commonly, though people notice a problem with both ears, known as diplacusis binauralis.
When you hear the same sound differently in each ear, it's usually related to pitch or timing. One ear may hear a sound at a different pitch and speed than the other ear.
Two main types of diplacusis
There are two subtypes of diplacusis binauralis:
- If you don't have problems with timing, and it's mostly different pitches you struggle with, it's a subtype known as diplacusis dysharmonica. This is the most common type of diplacusis.
- When ears hear sound at different speeds, it's a subtype known as diplacusis echoica. Because your ears are hearing things at different times, you may hear the same sound repeated as an echo.
What causes it?
Diplacusis can be a symptom of an underlying hearing or ear issue.
1. Hearing loss that's worse in one ear
Two types of hearing loss are especially linked to diplacusis:
- Hearing loss that's worse in one ear compared to the other, known as asymmetrical hearing loss.
- Hearing loss in only one ear, known as single-sided deafness or unilateral hearing loss
A 2016 study found that while hearing loss in general increased the likelihood of double hearing, it was most significant in people with asymmetrical hearing loss.
2. Sensorineural hearing loss
Sensorineural hearing loss is the most common type of hearing loss.It affects both ears evenly. It's often caused by aging or exposure to loud noise. Hearing loss can change the way you perceive sound frequencies, leading to diplacusis.
3. Obstructions in the ear
A blockage in the ear can alter sound perception and cause changes in hearing. Often times, once the blockage is removed, any hearing abnormalities will resolve. Potential obstructions or similar issues include:
- Ear infection
- Clogged ears or sinuses from a respiratory infection or allergies
- Excess earwax
- Eustachian tube dysfunction
- Tumor, such as acoustic neuroma
4. Head or ear trauma
Head or ear injuries can damage the inner ear structures (like the cochlea or auditory nerve) or disrupt sound processing in the brain. This may cause you to perceive the same sound at different pitches or frequencies.
5. Other causes
Additionally, double hearing may be the result of taking medications that are ototoxic (meaning they can damage the ear or vestibular disorders like Meinere's disease.
Musicians and diplacusis
Some research has indicated that musicians may be more likely to experience double hearing. A 2018 study found that classical musicians were more likely to report diplacusis than pop/rock musicians or non-musicians.
Musicians may be more vulnerable because they are at a higher risk of noise-induced hearing loss. They are also more inclined to notice symptoms as their ears are more sensitive to pitch and tone.

unique type of hearing condition.
Treatment options
The type of treatment you receive will depend on the cause, and may be a simple fix. For example, if your diplacusis is caused by an obstruction like earwax buildup or fluid from and infection, your hearing may return to normal once the obstruction is removed or the infection subsides.
If your double hearing is related to hearing loss, hearing aids may help you both hear better and balance sound input in both ears. Customized settings can help meet your individual hearing loss needs and can work to compensate for any asymmetrical hearing loss.
In cases of severe or profound hearing loss, cochlear implants may be recommended.
Other management techniques may involve:
- Auditory rehabilitation/auditory training to help your brain adapt
- Sound therapy or habituation which may help to desensitize you to the different pitches
- Cognitive behavioral therapy to help manage the stress accompanied with double hearing
How to get help for diplacusis
If you notice double hearing, promptly schedule a visit with a hearing healthcare or ENT physician.
They will evaluate your symptoms and will likely conduct a hearing test to determine if any issues are present and may also do additional testing like and auditory brainstem response (ABR) to check for any issues with the inner ear or auditory nerve that could be causing the distortion.
Visit our directory of consumer-reviewed hearing clinics to find a hearing aid specialist or audiologist near you.
The above is the interpretation of Diplacusis: Causes and Treatment for "Double Hearing" provided by Chinese hearing aid supplier Shenrui Medical. Link https://www.srmcm.com/Blog/Diplacusis_Causes_and_Treatment_for_Double_Hearing.html of this article is welcome to share and forward. For more hearing aid related information, please visit Blog or take a look at our Hearing aids products